KNN and Decision Trees Explained for Beginners
Learn K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) and Decision Trees in this beginner-friendly machine learning guide. Understand similarity-based learning, logical decision models, and how these core algorithms strengthen your ML foundation with practical examples from Neody IT.
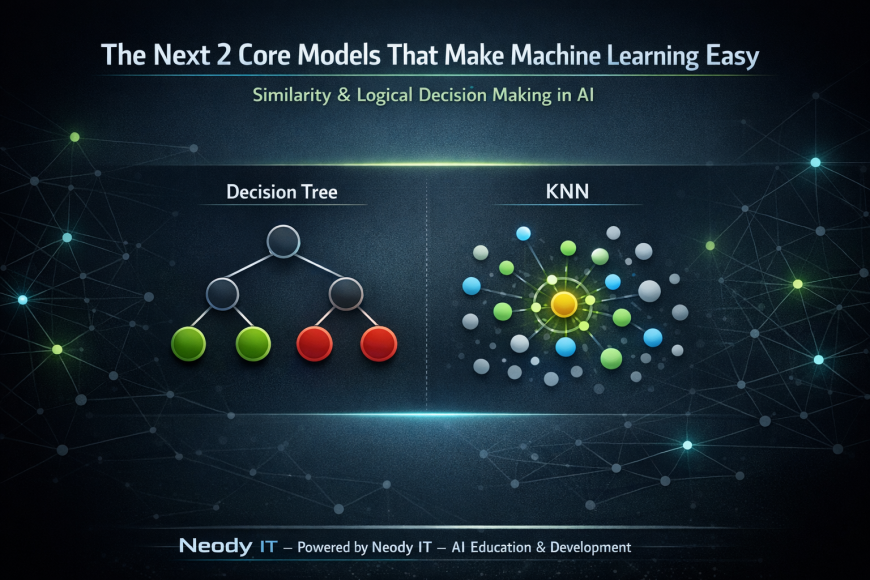
The Next 2 Core Models That Make Machine Learning Easy
A Beginner Guide to KNN and Decision Trees for Strong ML Foundations
Many beginners feel that Machine Learning becomes complicated very quickly. After learning about regression and classification basics, they often assume that advanced mathematics or deep neural networks are the next step.
At Neody IT, we consistently guide learners toward a different approach. Before moving into complex algorithms, beginners should understand models that make Machine Learning intuitive and logical.
This article introduces two core models that help build strong conceptual understanding:
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
Decision Trees
These models simplify Machine Learning by focusing on similarity and logical decision-making.
If you are following the learning journey from lofer.tech educational content, this is the next essential step in building your AI foundation.
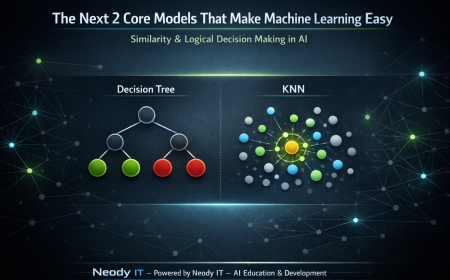
Model 3: K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
What is KNN?
K-Nearest Neighbors is one of the simplest Machine Learning algorithms. It classifies data based on similarity rather than complex equations.
The core idea is simple:
Similar data points belong to similar categories.
Instead of learning complicated rules during training, KNN compares new data with existing examples and decides based on similarity.
What Problem Does KNN Solve?
KNN is mostly used for classification problems, although it can also be applied to regression tasks.
Practical examples include:
Classifying fruits based on features like size, weight, or color
Recognizing handwritten digits
Recommending products similar to items a user already likes
In each case, the algorithm compares new input with known examples and identifies the closest matches.
How KNN Works Conceptually
KNN follows a simple process:
-
Choose a value for K, which represents how many neighbors to consider.
-
Measure the distance between the new data point and existing data points.
-
Identify the nearest K neighbors.
-
Check their categories.
-
Assign the majority category to the new data.
Important Beginner Concepts
Distance
Distance represents how close two data points are. Common measures include Euclidean distance.
Neighbors
These are the closest data points used to make predictions.
Majority Voting
The most common category among neighbors determines the final prediction.
Why KNN Is Important for Beginners
KNN is extremely beginner-friendly because:
It is easy to understand conceptually.
It demonstrates similarity-based learning clearly.
It does not require deep mathematical understanding initially.
Learning KNN helps beginners visualize how machines compare data rather than memorize formulas.
Model 4: Decision Tree
What is a Decision Tree?
A Decision Tree is a Machine Learning model that makes decisions step by step, similar to a flowchart.
Each step asks a question about the data and splits it into smaller groups until a final prediction is made.
You can think of it as a structured decision-making process.
What Problem Does Decision Trees Solve?
Decision Trees can handle both classification and regression problems.
Common real-world examples include:
Loan approval decisions
Customer churn prediction
Risk analysis in finance or healthcare
The model learns decision rules automatically from data.
How Decision Trees Work Conceptually
Decision Trees split data into branches based on conditions.
For example:
Is age greater than 30?
Is income above a certain level?
Has the customer purchased before?
Each split creates branches that lead toward a final decision.
Important Beginner Concepts
Nodes
Points where decisions are made.
Branches
Paths that represent possible outcomes.
Splits
Conditions used to divide data.
Information Gain
A measure that helps the model decide which split is most useful. Beginners only need basic awareness of this idea.
Why Decision Trees Are Powerful
Decision Trees are widely loved by beginners because:
They are visual and easy to interpret.
They show how machines make logical decisions.
They help learners understand how models break down complex problems into smaller steps.
This makes Machine Learning feel less abstract and more understandable.
How These Four Models Build Your Machine Learning Foundation
If you have followed the learning sequence recommended by Neody IT, you now understand four essential models:
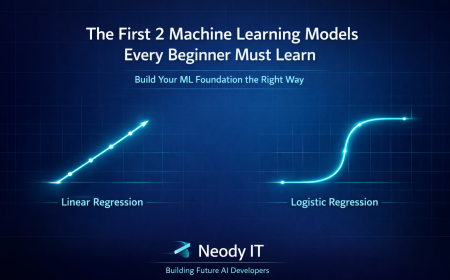
Linear Regression predicts numerical values.
Logistic Regression handles yes or no classification problems.
KNN focuses on similarity-based learning.
Decision Trees use logical rule-based decision making.
Together, these models introduce core Machine Learning ideas:
Regression
Classification
Pattern recognition
Decision logic
Once these concepts are clear, most Machine Learning algorithms become easier to understand because they build upon the same underlying principles.
What You Should Do Next
To strengthen your Machine Learning foundation:
Understand regression versus classification clearly.
Study these four models conceptually before diving into advanced topics.
Implement them using Scikit-Learn to see how they work in practice.
Experiment with small datasets.
Compare results across different models to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
Hands-on experimentation combined with conceptual clarity accelerates learning significantly.
Final Thoughts
Machine Learning becomes much easier when approached step by step.
Instead of jumping into complex deep learning models, focus first on intuitive algorithms that reveal how machines actually learn.
At Neody IT, we encourage beginners to build clarity before complexity. Mastering Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, KNN, and Decision Trees gives you a complete foundational toolkit.
With these models understood, advanced Machine Learning will feel logical rather than overwhelming.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
1
Love
1
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0